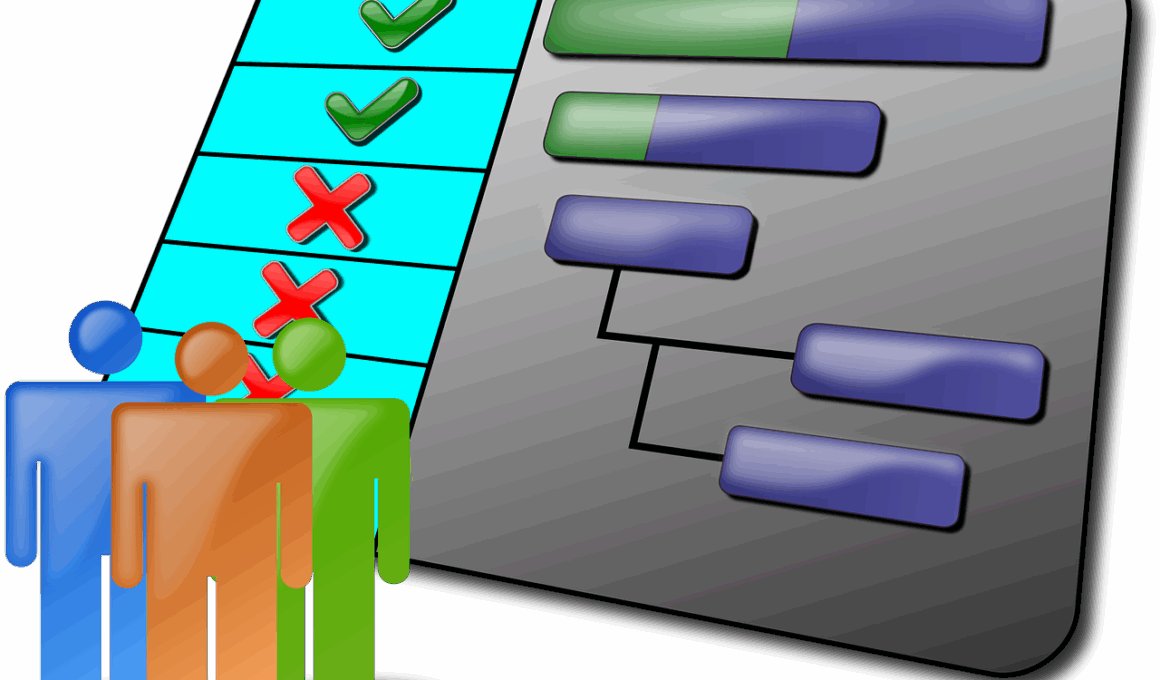
An Introduction to Gantt Charts: Visualizing Your Project Timeline
Gantt charts are invaluable tools in project management, providing a visual overview of tasks within a project. These charts illustrate a timeline with horizontal bars representing various tasks necessary to complete a project. Each bar signifies a task’s start date, duration, and end date. By visually plotting these elements, teams can monitor progress, identify hot areas, and manage resources effectively. Implementing Gantt charts simplifies communication among stakeholders, ensuring everyone stays aligned on project timelines and expectations. Their straightforward presentation makes it easy to spot overlapping tasks that could potentially cause delays. Hence, teams can proactively adjust schedules to mitigate risks. Furthermore, Gantt charts are instrumental in resource allocation, enabling project managers to visualize the workload of team members. This awareness assists in balancing assignments fairly, which is critical for team morale and productivity. In essence, Gantt charts serve as a comprehensive communication tool between project managers and team members, boosting collaboration and understanding. The usefulness of Gantt charts extends across various industries, from construction to software development, ensuring they remain a staple in the toolkit of any effective project manager.
Constructing a Gantt chart is relatively straightforward, making it an approachable tool for those new to project management. First, outline the tasks required to complete your project. This can include everything from initial research to final evaluation. Next, determine the duration of each task, ensuring realistic estimations based on past experiences or data. Once you’ve got a comprehensive list of tasks and their durations, the next step is to organize them in a sequential order. This step is essential, as it lays the foundation for understanding how different tasks interplay throughout the project timeline. Afterward, you can begin creating the actual Gantt chart. Utilize project management software or traditional tools like Microsoft Excel to plot the timeline visually. Input the tasks along the vertical axis, while the horizontal axis represents the timeline, detailing start and end dates. With this information at hand, input the tasks as horizontal bars that fill the requisite time span. When completed, the Gantt chart becomes a living document, updated regularly to reflect actual progress versus planned timelines, thus granting clear insights into the project’s status.
Benefits of Gantt Charts in Project Scheduling
Gantt charts bring numerous benefits to project scheduling, significantly enhancing operational efficiencies and transparency. One of the most substantial advantages is that they provide clarity regarding task dependencies and timelines. By visualizing how tasks relate and overlap, teams can better understand critical paths and avoid potential bottlenecks. This visibility reduces confusion, ensuring that all team members grasp their roles and responsibilities. Furthermore, Gantt charts promote accountability among team members, as each individual can see how their progress contributes to overall project objectives. Because of this shared visibility, teams can collaborate more effectively, responding quickly and efficiently to challenges and changes. Another notable benefit is that Gantt charts enable improved time management, allowing project managers to allocate resources more judiciously, recognizing when adjustments are needed. Additionally, regular updates of the Gantt chart foster a culture of communication and engagement throughout the project lifecycle, keeping stakeholders informed and investments in check. When executed correctly, Gantt charts lead to successful project outcomes, reduced project durations, and targeted delivery of results, ultimately increasing satisfaction for clients and stakeholders alike.
Despite their advantages, Gantt charts also come with specific limitations that project managers should consider. One of the primary downsides is that they can become unwieldy for complex projects with numerous tasks. The more tasks present in a Gantt chart, the thicker and more crowded it becomes, making it difficult to discern critical relationships and actual timelines. Additionally, traditional Gantt charts lack detail regarding resource allocation, making it tough to monitor who is responsible for each task. In technology-driven environments, advanced project management software may be more appropriate than traditional Gantt representations, which can lead to information overload or confusion among team members. Furthermore, Gantt charts may not adapt well to changing project scopes or timelines, requiring manual updates that can be time-consuming and error-prone. Rapidly adapting to project changes is crucial in project management; thus, reliance solely on Gantt charts may hinder agility. As with any tool, balancing Gantt chart usage with other project management methodologies is essential, ensuring that the right tools are utilized for optimal project efficiency and success.
When to Use Gantt Charts
Knowing when to implement Gantt charts effectively is critical for maximizing their benefits in your project management endeavors. These charts are best utilized in projects characterized by clear timelines, defined tasks, and interdependencies. For instance, if your project involves a series of steps that depend on the completion of prior tasks, a Gantt chart offers the clarity needed to navigate these dependencies smoothly. Additionally, Gantt charts shine in projects that require precise tracking of timelines and progress monitoring, enabling teams to adjust quickly if delays occur. They are particularly beneficial for projects involving multiple stakeholders, where visual representation enhances communication and stakeholder engagement. However, if your project is shorter with simpler tasks and fewer dependencies, a Gantt chart may be unnecessary and overly complicated. In these cases, traditional to-do lists or Kanban boards may be more effective. It’s crucial to assess the specific project characteristics and determine whether incorporating a Gantt chart aligns with the overall project strategy, ensuring efficient use of available management tools without adding unnecessary complexity.
Project managers must understand that Gantt charts are not static; they are dynamic documents that require ongoing maintenance and updates to remain effective. Tracking actual progress against the planned timelines is essential for ensuring that the project adheres to its schedule. Regular updates prevent misalignment among team members, fostering transparency and trust. When tasks fall behind schedule, it’s important to analyze the reasons for the delay and, if necessary, adjust the project timeline accordingly. This iterative update process allows the Gantt chart to remain a reliable resource, offering a real-time snapshot of project progress. As the project evolves, project managers should revisit initial task assessments to determine if adjustments are required based on emerging challenges or opportunities. Effective communication is key; team members should feel empowered to provide updates and share insights, creating a collaborative environment. By maintaining the Gantt chart as a living document, project managers can better engage stakeholders, demonstrating accountability, adaptability, and a commitment to project success. Thus, an updated Gantt chart significantly contributes to achieving project goals efficiently.
Conclusion: Mastering Gantt Charts for Successful Projects
In conclusion, mastering Gantt charts is crucial for anyone looking to manage projects successfully. These versatile tools not only visualize project timelines but also enhance communication and collaboration among teams. By breaking down tasks and clarifying dependencies, Gantt charts serve as powerful aids in identifying potential risks and maintaining accountability. A well-constructed Gantt chart fosters a culture of ownership within project teams, encouraging members to stay on track and meet their deadlines. While challenges exist with their complexity and adaptability, understanding how to use them effectively can greatly minimize these issues. Project managers should prioritize regular updates and a collaborative approach to utilizing Gantt charts, promoting efficacy and engagement. Although Gantt charts may not fit every project’s needs perfectly, they are indispensable in environments where clear timelines and accountability are critical. Ultimately, becoming proficient with Gantt charts can lead to a more organized project management style, enabling timely delivery, stakeholder satisfaction, and achievement of project objectives. Learning how to harness the full potential of Gantt charts will undoubtedly yield significant benefits for project success and team dynamics.