Use of Renewable Energy in Food Manufacturing Plants
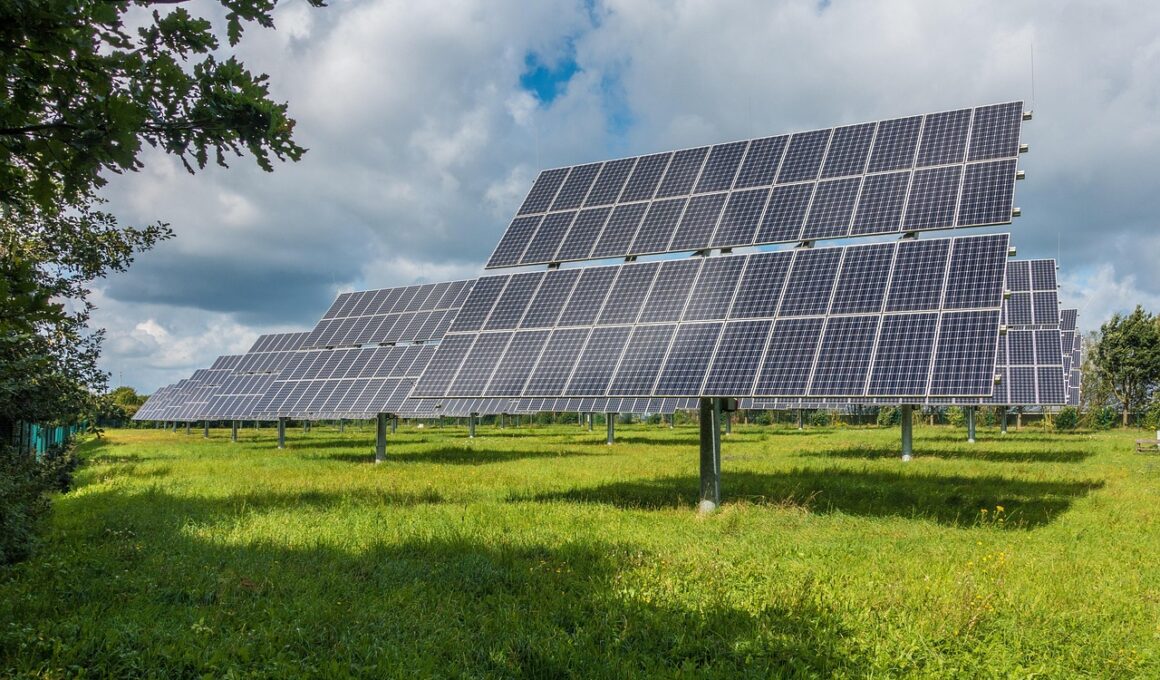
The food manufacturing industry increasingly turns to renewable energy sources to enhance its sustainability goals. By adopting solar, wind, or biomass energy, facilities can significantly reduce their carbon footprint. Renewable energy not only cuts greenhouse gas emissions but can also stabilize energy costs over time. As businesses invest in renewable technologies, the long-term savings can help offset the initial capital expenses. Notably, these investments align with consumer preferences toward sustainable products. Studies show that consumers are willing to pay premium prices for foods produced using sustainable methods. Moreover, renewable energy provides a reliable energy supply, essential for maintaining production continuity. Consequently, food manufacturers can operate more efficiently while contributing to environmental protection. Additionally, using renewable energy often leads to a positive brand image, encouraging a stronger connection with eco-conscious consumers. Through innovative partnerships and programs, the industry can leverage renewable energy generation effectively. Maximizing on-site energy production can even create surplus energy for local communities. This shift not only reduces dependency on fossil fuels but also promotes a renewable and sustainable future for food manufacturing. In conclusion, adopting renewable energy is a smart, sustainable strategy for the evolving food industry.
Types of Renewable Energy Sources
Food manufacturing plants can choose from various renewable energy sources to meet their operational needs. Solar energy remains among the most popular choices due to its accessibility and decreasing installation costs. With solar panels installed on rooftops or available as standalone solar farms, manufacturers can harness this abundant resource. Additionally, wind energy is another viable option, especially in areas with consistent wind patterns. Wind turbines can generate substantial amounts of electricity, providing a clean and reliable energy source for facilities. Biomass energy, derived from organic materials, also offers an attractive alternative. It utilizes waste products from food processing to create energy, further promoting a circular economy within the industry. Hydropower, while less common in food manufacturing, can also serve as a renewable energy source when suitable water resources are available. Geothermal energy is yet another innovative option, utilizing the earth’s natural heat to generate power. Each renewable energy source has its unique advantages and challenges, necessitating careful consideration by manufacturers. By diversifying energy sources, food manufacturers can enhance reliability while improving sustainability practices across production processes.
Implementing renewable energy solutions requires significant planning and investment by food manufacturers. To ensure successful integration, companies must conduct comprehensive feasibility studies to evaluate their energy needs and the viability of potential renewable sources. Identifying specific energy consumption patterns helps facilities determine the most effective renewable energy systems to install. Companies should analyze financial aspects, including payback periods and potential incentives from government programs. Utilizing grants or tax credits can ease the financial burden associated with renewable energy projects. Additionally, close collaboration with technology providers facilitates the selection of appropriate renewable technologies that fit operational requirements. Monitoring and evaluating performance after implementation contributes to optimizing energy management strategies. Companies increasingly utilize energy management software to track energy usage, helping identify areas for improvement. This data-driven approach allows manufacturers to respond quickly to energy demands while minimizing waste. Companies can enhance their production efficiency by continuously analyzing energy consumption patterns and adjusting methods accordingly. Furthermore, engaging employees in sustainability initiatives fosters a culture of energy awareness that contributes to long-term improvements. In this way, renewable energy becomes integral to the food manufacturing ecosystem, driving progress toward a more sustainable future.
Challenges in Transitioning to Renewable Energy
Transitioning to renewable energy sources poses several challenges for food manufacturing plants. One significant barrier is the initial capital investment required for renewable energy installations, which can be substantial. Despite potential long-term cost savings, companies may hesitate to commit significant resources upfront. Additionally, businesses may encounter resistance from stakeholders who are skeptical regarding the feasibility of renewable energy systems. Addressing these concerns through education and transparency can help build support for energy transitions. Technical barriers may arise when integrating renewable energy technologies into existing infrastructure. Food manufacturers must upgrade their systems to accommodate different energy sources while ensuring efficiency and reliability. Furthermore, fluctuating energy production from renewable sources can complicate supply requirements, necessitating energy storage solutions or backup systems. Weather variability affects solar and wind energy generation, requiring plants to develop contingency plans for energy shortages. Regulatory constraints can also pose challenges, especially in navigating the permitting process for renewable energy projects. Despite these obstacles, many food manufacturers are finding it increasingly important to pursue renewable energy as part of a broader commitment to sustainability. Persistence and proper planning enable plants to overcome these hurdles and successfully adopt renewable energy practices.
Engaging in renewable energy initiatives not only results in environmental benefits but has significant social implications for food manufacturing plants. By prioritizing renewable energy, manufacturers can enhance their corporate social responsibility (CSR) profiles, showcasing their commitment to sustainability and community engagement. This responsibility resonates with consumers who are increasingly looking for brands that reflect their values. Additionally, investments in renewable energy can lead to job creation in the local community, supporting economic development. As renewable energy projects grow, new roles in technology, maintenance, and operations emerge, benefiting local job markets. Collaboration with local governments and organizations can further enhance community participation in renewable energy initiatives. Manufacturers can offer educational workshops or partnerships to raise awareness about sustainability. Encouraging employee involvement in environmental initiatives fosters a culture of sustainability within organizations. Engaging employees helps create advocates who are passionate about promoting renewable energy practices both at work and in their communities. As food manufacturing plants embrace renewable energy, they position themselves as leaders in sustainability, reinforcing brand loyalty and gaining competitive advantages. This engagement extends financial and ethical benefits, creating a win-win situation for both manufacturers and the communities they serve.
The Future of Renewable Energy in Food Manufacturing
As renewable energy technologies continue to advance, their application within the food manufacturing sector is expected to grow significantly. Innovations in energy storage solutions enable manufacturers to harness renewable energy more effectively. Improved battery technologies allow storage of excess generated energy, making it available when production demands dictate. Additionally, ongoing research and development are driving down the costs of renewable energy systems, facilitating wider adoption. As food manufacturers prioritize sustainability, partnerships with energy providers and technology developers become increasingly crucial in driving change. Incorporating innovative energy solutions will enable manufacturers to meet their production goals while minimizing environmental impacts. Furthermore, national policies promoting renewable energy adoption may create additional incentives for companies to integrate green practices. Forecasts indicate a rapid shift toward renewable energy sources as food manufacturers respond to evolving regulations and consumer demands. The expansion of renewable energy in the food industry signifies a transformational moment. As these companies transition toward sustainable practices, we can expect to see lasting changes in energy consumption patterns. Sustainability and corporate responsibility will become central tenets. Overall, the future of renewable energy in food manufacturing appears optimistic, with significant potential for positive impacts across the industry.
In conclusion, the integration of renewable energy in food manufacturing plants represents a crucial step toward a more sustainable future. Companies can significantly reduce their environmental footprints through the adoption of solar, wind, biomass, and other renewable energy sources. However, this transition requires careful planning, investment, and collaboration among various stakeholders. Overcoming financial, technical, and regulatory challenges plays an essential role in the successful adoption of these new practices. As food manufacturers engage in renewable energy initiatives, they not only strengthen their sustainability efforts but also improve their social responsibility profiles. By contributing to their local economies and engaging communities, these manufacturers can foster public trust and loyalty. Furthermore, the future of renewable energy in food manufacturing is bright, driven by advancements in technology and shifting consumer expectations. Companies that prioritize sustainability and renewable energy can gain a competitive edge in the marketplace. The transition towards renewable energy also signifies a broader movement within the food industry toward environmental stewardship. In this way, renewable energy will become a cornerstone of sustainable food manufacturing practices, ultimately benefiting the planet, consumers, and future generations.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the integration of renewable energy in food manufacturing plants represents a crucial step toward a more sustainable future. Companies can significantly reduce their environmental footprints through the adoption of solar, wind, biomass, and other renewable energy sources. However, this transition requires careful planning, investment, and collaboration among various stakeholders. Overcoming financial, technical, and regulatory challenges plays an essential role in the successful adoption of these new practices. As food manufacturers engage in renewable energy initiatives, they not only strengthen their sustainability efforts but also improve their social responsibility profiles. By contributing to their local economies and engaging communities, these manufacturers can foster public trust and loyalty. Furthermore, the future of renewable energy in food manufacturing is bright, driven by advancements in technology and shifting consumer expectations. Companies that prioritize sustainability and renewable energy can gain a competitive edge in the marketplace. The transition towards renewable energy also signifies a broader movement within the food industry toward environmental stewardship. In this way, renewable energy will become a cornerstone of sustainable food manufacturing practices, ultimately benefiting the planet, consumers, and future generations.