Kanban vs Scrum: Choosing the Right Agile Approach
In the dynamic realm of agile methodologies, both Kanban and Scrum offer effective strategies for project management. Each framework caters to distinct workflow patterns and project demands. Understanding the fundamental differences can facilitate better choice-making for teams. Kanban is particularly advantageous for continuous flow and visualizing work stages. It promotes maintaining an optimal work-in-progress limit to ensure maximum efficiency. In contrast, Scrum is ideal for teams operating in sprints, typically lasting two to four weeks, allowing for quick iterations and assessments. This method focuses on roles, events, and artifacts to ensure disciplined processes. The choice between these frameworks largely depends on project complexities and the desired flexibility level. Kanban favors adaptability by enabling teams to make real-time changes, whereas Scrum emphasizes a structured approach with specific roles like Scrum Master and Development Team. Ultimately, both methods serve the goal of enhancing productivity, though the application of each varies significantly with project type. Aligning your team’s workflow with the right framework enhances overall productivity and project delivery success, enabling more consistent results and team satisfaction.
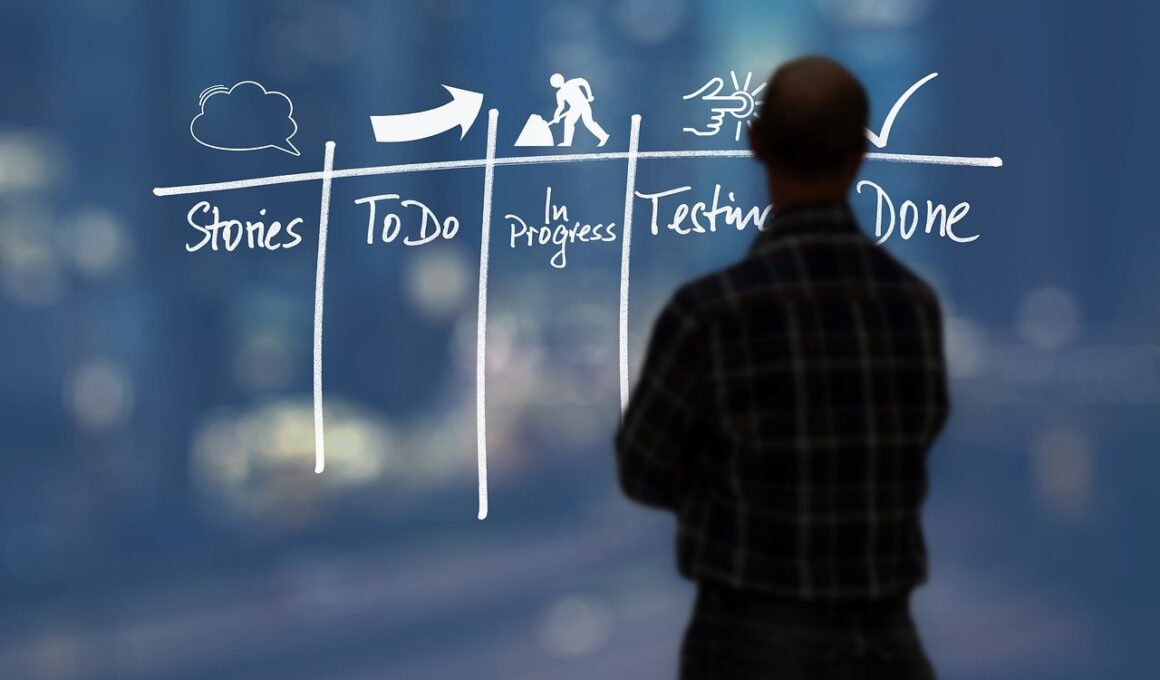
Understanding Kanban’s Efficiency
Kanban utilizes visual boards to represent tasks in progress, completed tasks, and upcoming work items. This transparency promotes accountability among team members. When a task moves to done, it signifies accomplishment, inspiring team motivation. The Kanban approach leads to gradual and incremental improvements in workflow efficiency. Teams can prioritize tasks effectively based on urgency and client needs. Moreover, Kanban works well with changing priorities, making it extensively valuable in dynamic environments. Unlike Scrum, it does not require iterations, allowing teams to adapt swiftly without pre-defined time-boxed constraints. Implementing WIP limits aids in identifying bottlenecks proactively. This agile flow helps teams focus on completing work before taking on additional tasks, fostering a culture of completion. Tools like Trello or Jira can support Kanban’s implementation, making task management seamless. Frequent feedback gathering encourages stakeholder involvement, improving deliverable quality. The approach is highly suitable for maintenance projects where efficiency and rapid response times are crucial, making Kanban a commendable choice for ongoing operations. Adaptability and flexibility are hallmark traits of successful teams leveraging Kanban’s efficient methodology.
On the other hand, Scrum’s structured framework emphasizes roles and ceremonies designed to boost team collaboration and accountability. Scrum comprises a Product Owner who defines the vision, and the Development Team responsible for delivering increments of work. The Scrum Master facilitates the process, ensuring the team adheres to Scrum principles. This clear distribution of roles significantly enhances coordination and communication among team members, contributing to effective project outcomes. The process begins with Sprint Planning, where teams outline goals for the sprint duration. Daily stand-up meetings provide an opportunity to discuss ongoing tasks and obstacles, promoting transparency. After each sprint, a retrospective reflects on process improvements, reinforcing a culture of continuous growth. This iterative approach allows teams to assess progress and adapt strategies regularly. The emphasis on predefined time frames helps maintain team momentum while delivering tangible results. For projects with strict deadlines and clear requirements, Scrum proves to be exceptionally beneficial. As teams adapt, they become more proficient in delivering quality outputs consistently, showcasing Scrum’s capability to handle complex projects effectively.
Comparing Flexibility and Structure
The decision-making process between Kanban and Scrum influences not just productivity but also team dynamics. Kanban’s flexible nature accommodates diverse teams, allowing members to determine their workflow. In contrast, Scrum imposes a structure that may initially seem rigid but can enhance performance in teams comfortable with defined roles. Flexibility in Kanban makes it appealing for ongoing tasks and non-project-based work, crucial for service-oriented teams. Scrum, on the other hand, may suit development teams better with concrete timelines and outcomes. However, it requires a commitment to follow the framework strictly, while Kanban draws on existing workflows, integrating enhancements organically. Continuous improvement is embedded in both methodologies, although Kanban fosters evolutionary changes while Scrum opts for more defined adjustments. Ultimately, teams need to evaluate their current workflows, project types, and internal cultures. Collaborating on which methodology aligns with their goals makes the transition smoother. The effectiveness of either approach largely depends on the team’s adaptability to change and willingness to adhere to the chosen methodology.
Adopting either Kanban or Scrum is not a matter of one size fits all; rather, it aligns with team preferences, project nature, and organizational culture. As agile methodologies increasingly gain traction, organizations might integrate practices from both frameworks, crafting a hybrid approach tailored to specific operational needs. This responsive strategy highlights that tools should complement team dynamics rather than constrain them. Experimenting with both methodologies through pilot projects can uncover strengths in each, enabling teams to determine the best fit for their unique contexts. Flexibility remains crucial in agile transformation, ensuring teams aren’t boxed into a single approach. By allowing experimentation, organizations can tap into the benefits of both Kanban and Scrum, optimizing workflows and fostering a culture of collaboration. Collaboration across teams in defining processes allows for enhanced efficiency and productivity. Each project phase offers learning opportunities, emphasizing the importance of feedback and reflexive practices. Embracing this mindset allows agile teams to thrive, adapting and evolving as required. Ultimately, assessing results and adjusting accordingly paves the way for continuous improvement and success in agile project management.
Implementation Challenges and Considerations
While Kanban and Scrum promise numerous advantages, teams encounter hurdles during implementation. Resistance to change often arises as teams adapt to new processes, requiring robust change management practices. Training all team members on the selected methodology is crucial for effective adoption, ensuring everyone understands the framework’s principles and practices. This education period allows a smoother transition by aligning expectations and reducing confusion. Establishing clear objectives for Kanban or Scrum based on project needs enhances focus, aligning the team’s efforts with organizational goals. Additionally, it’s essential to continually analyze and assess the chosen methodology’s effectiveness. Regular check-ins and retrospectives help identify bottlenecks, improving team awareness of the issues encountered. Developing a culture that values transparency encourages open discussions about challenges, enabling teams to address them swiftly. Moreover, incorporating feedback mechanisms fosters a sense of ownership among team members, leading to greater commitment towards the adopted approach. Ultimately, addressing these challenges head-on facilitates a more seamless integration of Kanban or Scrum, promoting sustained agility and efficiency in project management.
In conclusion, the choice between Kanban and Scrum hinges on understanding both methodologies’ unique principles and practices. Organizations must evaluate project types, team capacities, and stakeholder expectations before making a decision. Kanban provides a compelling framework for continuous flow, adapting to variable workloads, while Scrum excels in delivering iterative increments in structured timeframes. The decision should reflect the organization’s culture and project demands, ensuring optimal alignment between workflow and methodology. By embracing the right approach, teams can enhance their performance, foster collaboration, and improve overall project outcomes. Each framework is not inherently better; rather, their effectiveness lies in harmonizing with team dynamics and particular objectives. Training members adequately on their chosen framework promotes a smooth transition, minimizing initial resistance. Continuous evaluation reinforces the process of refinement and enhancement. As they evolve in their agile journey, teams can develop a hybrid model that optimally combines elements from both methodologies based on contextual needs. Striving for improvement and adaptation should remain constants in the pursuit of successful project management.